Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer
We organize your Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer in Germany
With Germany Health you can find the best clinics when you are interested in undergoing for dendritic cell vaccines for cancer in Germany. Immunotherapy for cancer is available at clinics and centers with certification and licenses in Germany only. University hospitals don’t to it.
We offer only hand-picked, certified, and trusted clinics for dendritic cell vaccines for cancer in Germany and Immunotherapy for Cancer in Germany.
By today the German clinic offers a high standard of medical care. The doctors there have 20+ years of experience in treating patients in Germany with dendritic cell vaccines for cancer.
What is cancer?
Cancer is a disease that happens when cells in the body grow and divide in an uncontrolled way. Normally, our cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly manner, but in cancer, something goes wrong. The cells don’t stop growing when they should, and this can lead to lumps or masses called tumors. Some cancers, though, don’t form tumors; they can spread through the blood or lymph system.What makes cancer tricky is that it can start in any part of the body and spread to other areas. For example, breast cancer starts in the breast, while lung cancer starts in the lungs. Sometimes, cancer is found early, and it can be treated more easily. Other times, it’s harder to find and treat, which is why regular check-ups and screenings are so important.
Cancer treatments have come a long way in recent years, with options like surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and dendritic cell vaccination for cancer. While it can be a tough journey, many people do recover and go on to live healthy, happy lives.
What can cause cancer
Cancer happens when cells in the body start growing uncontrollably, and this growth doesn’t follow the normal process. Normally, our cells divide, grow, and die in an orderly fashion, but sometimes, something goes wrong. The causes of cancer are complex, and they can vary from person to person, but there are several key factors that contribute to the development of cancer.However, one of the main causes is genetic mutations. These are changes in the DNA of a cell, and they can happen for various reasons. Thus, sometimes, these mutations happen because of external factors, like smoking, sun exposure, or certain chemicals. These factors can damage the DNA and trigger cancer. Other times, mutations are inherited from family members, which is why some cancers run in families.
Another factor is lifestyle choices. Smoking, for example, is strongly linked to lung cancer and other respiratory cancers. A poor diet, lack of exercise, and being overweight can increase the risk of cancers like colon, breast, and liver cancer. Additionally, exposure to environmental toxins, like pesticides or industrial chemicals, can also contribute to cancer development.
Thus, age is another significant factor. As we get older, our cells have had more time to accumulate mutations, which increases the chances of developing cancer. However, cancer can affect people of all ages, and younger people can be at risk too.
Of course, exciting advancements in cancer treatment include dendritic cell vaccines in Germany. Therefore, this form of immunotherapy aims to train the body’s immune system to recognize and fight cancer more effectively.
Dendritic cell vaccines can help boost the immune system’s ability to target cancer cells, offering hope for new and more personalized treatment options for those battling cancer. Dendritic cell-based vaccines shows promise as a treatment option that could make a difference in fighting cancer.
Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer with Other Immunotherapies
1. Boosting Cancer Treatment with Dendritic Cell Vaccines in Germany
Cancer treatment has come a long way in recent years, with immunotherapy emerging as a promising option. As a result, immunotherapy for cancer works by harnessing the body’s own immune system to fight cancer more effectively. Among the various forms of immunotherapy, dendritic cell vaccines for cancer stands out as a novel and powerful approach.
Hence, combining conventional type dcs, though dendritic cell vaccines for cancer in Germany with other types of immunotherapies, doctors are offering patients more effective, personalized treatment strategies with fewer side effects. In this article, we will explore the advantages of combining dendritic cell vaccines for cancer with other immunotherapies, and also look at the different types of immunotherapies available today.
2. A Multi-Faceted Approach: How Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer Can Work with Other Immunotherapies
Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, with new therapies emerging every year. Dendritic cell vaccination for cancer is an immunotherapy that takes a patient’s dendritic cells (a type of immune cell) and trains them to recognize and target cancer cells.
This process makes the immune system more effective at fighting the cancer. However, cancer can be complex, and a single therapy may not always be enough to completely eliminate it. This is where combining dendritic cell vaccination with other immunotherapies can offer significant advantages.
Understanding Dendritic Cell Vaccines
Dendritic cell vaccination for cancer works by using the patient’s own dendritic cells, which are responsible for detecting foreign invaders like bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells. These cells are collected from the patient, then exposed to the cancer cells in a lab to “teach” them to recognize and target the cancer.
Once trained, the dendritic cells are reintroduced into the patient’s body, where they stimulate a more robust immune response against the cancer. The advantage of this method is that it boosts the patient’s natural immune system to fight cancer, potentially with fewer side effects than traditional treatments like chemotherapy or radiation.
One of the unique advantages of dendritic cell vaccination for cancer is its ability to tailor the treatment specifically to the individual’s cancer. By focusing on the unique features of each patient’s tumor, dendritic cell therapy can be personalized, increasing the chances of success.
Combining Dendritic Cell Vaccines with Other Immunotherapies
Cancer is a complex disease, and often, no single treatment is enough to defeat it. That’s why doctors often combine different treatments to increase their chances of success. The idea behind combining dendritic cell vaccines in Germany for cancer with other immunotherapies is to target the cancer from multiple angles. Let’s take a look at some of the most common types of immunotherapies and how they can work with dendritic cell therapy.
1. Checkpoint Inhibitors
One of the most well-known forms of immunotherapy is the use of checkpoint inhibitors. Checkpoints are proteins on immune cells that act as brakes, preventing the immune system from attacking normal cells. Cancer cells can hijack these checkpoints to avoid being recognized by the immune system.
Checkpoint inhibitors are drugs that block these proteins, releasing the brakes on the immune system and allowing it to attack cancer cells.
When dendritic cell therapy for cancer is combined with checkpoint inhibitors, the results can be significantly enhanced. Dendritic cells are trained to recognize cancer cells, and checkpoint inhibitors remove the blocks that prevent the immune system from attacking these cells. This combination can lead to a more aggressive immune response and, in some cases, a better chance of eradicating the cancer.
Examples of checkpoint inhibitors include:
– Pembrolizumab (Keytruda): Used for cancers such as melanoma, lung cancer, and head and neck cancers.
– Nivolumab (Opdivo): Approved for use in melanoma, lung cancer, kidney cancer, and more.
2. Cytokine Therapy
Cytokines are proteins that help regulate the immune system’s response to infections and cancer. They act as signaling molecules, helping immune cells communicate and coordinate their efforts. Some types of cytokines, like interleukins and interferons, are used in cancer therapy to stimulate the immune system.
When combined with dendritic cell vaccination for cancer, cytokines can help amplify the immune response, making dendritic cells even more effective at attacking cancer cells. By enhancing the overall activity of immune cells, this combination therapy can help the body fight off the cancer more effectively.
Examples of cytokine therapies include:
– Interleukin-2 (IL-2): Often used in the treatment of kidney cancer and melanoma.
– Interferon-alpha Used for certain types of leukemia and melanoma.
3. Cancer Vaccines
Cancer vaccines are another type of immunotherapy for cancer designed to boost the body’s immune response to cancer. Unlike traditional vaccines that prevent infection, cancer vaccines are used to treat cancer by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight the cancer cells.
Hence, combining dendritic cell vaccination for cancer with cancer vaccines can create a powerful synergy. While the cancer vaccine helps train the immune system to recognize the cancer, dendritic cell therapy amplifies this response by directly engaging immune cells in a more targeted way. Together, these treatments work to strengthen the body’s ability to fight cancer.
6. T-Cell Therapy (Including CAR-T)
T-cell therapy involves modifying a patient’s own T-cells (a type of immune cell) to recognize and attack cancer cells. One of the most advanced forms of T-cell therapy is CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy), which involves modifying T-cells with special receptors that allow them to recognize cancer cells more easily.
When combined with dendritic cells, T-cell therapy can be even more effective. While T-cells are specifically engineered to target cancer cells, dendritic cells can further help the immune system by training the body to better recognize and destroy the cancer. This combination of therapies can be a highly effective way to treat cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
Examples of T-cell therapies include:
– Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel): A CAR-T therapy used to treat certain types of leukemia and lymphoma.
– Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel): Another CAR-T therapy for lymphoma.
How Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer Works with Other Immunotherapies
When dendritic cell vaccination is combined with other immunotherapies, the effects are often greater than when either therapy is used alone. Here’s how they work together:
– Complementary Actions: Dendritic cells train the immune system to recognize and target cancer, while other immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors, remove the natural barriers preventing the immune system from attacking the cancer.
– Amplified Immune Response: Immunotherapies like cytokines or T-cell therapy can enhance the activity of immune cells, making them more effective at fighting cancer. Dendritic cells serve as a catalyst, helping these immune cells work more efficiently.
– Targeting Multiple Pathways: Cancer cells are adept at evading the immune system, and they often use multiple mechanisms to do so. By combining different immunotherapies, doctors can attack cancer from several angles, making it more difficult for the cancer to resist treatment.
Conclusion of combined immunotherapies for cancer treatment
The combination of dendritic cell vaccines for cancer with other immunotherapies offers many advantages in the fight against cancer. Hence, by using multiple therapies that target different aspects of the immune response, doctors can provide a more personalized, comprehensive treatment plan that is more effective at fighting cancer.
Whether it’s through checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, cytokine therapy, cancer vaccines, or T-cell therapies, combining these treatments with dendritic cell therapy offers new hope for patients with cancer. The goal is not just to treat cancer, but to help the body’s own immune system fight it off in a more powerful and lasting way.
Immunotherapy for Cancer in Germany
Therapies that enhance the body’s natural methods of fighting cancer are being studied by scientists around the world. Unfortunately, cancer is the leading cause of premature death. However, yet only two Nobel Prizes in Medicine have been awarded to cancer researchers in the last 15 years – both for immunotherapy (2011 R Steinman, 2018 P Allison, and T Honjo).Hence, if there’s any hope in the fight against cancer, it’s in immunotherapy for cancer. While Allison and Honjo use specific chemotherapy to make cancer cells vulnerable through the immune system, Steinman strengthens the immune system to discover cancer cells naturally – through dendritic cell vaccination (DCV).
This approach teaches the body’s immune system to seek out and destroy cancer cells. Because it is a natural process, Dendritic Cell Vaccination does not cause any lasting side effects. However, this should cause induced immune responses in patients.
Immunotherapy, a groundbreaking approach in cancer treatment, leverages the body’s immune system to fight malignancies. Therefore, among its various forms, dendritic cell (DC) immunotherapy for cancer stands out due to its potential to induce a robust and specific immune response against tumors.
Dendritic cells, key players in the immune system, act as messengers that present antigens to T cells, thereby initiating and regulating adaptive immune responses. Utilizing these cells in immunotherapy for cancer aims to enhance the body’s natural ability to combat cancer.
The Role of Dendritic Cells in Immunotherapy
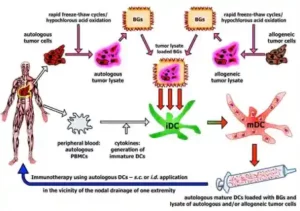
Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) essential for triggering T cell responses. They capture antigens from pathogens or tumor cells and process them into smaller fragments. These fragments are then displayed on the cell surface, bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. This presentation is critical for the activation of T cells, which then proliferate and attack the antigen-bearing cells.
In the context of immunotherapy for cancer, dendritic cells are harnessed to amplify this natural process. Hence, the typical procedure involves isolating dendritic cells from the patient’s blood, loading them with tumor antigens, and then reintroducing them into the patient. This primes the immune system to recognize and target cancer cells more effectively.
- Preparation of Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy for Cancer
However, the process begins with the collection of monocytes from the patient’s blood through leukapheresis. These monocytes are cultured and differentiated into dendritic cells in the laboratory using specific growth factors. Once mature, the dendritic cells are exposed to tumor antigens. Therefore, these antigens can be derived from various sources, such as tumor lysates, peptides, or proteins specific to the cancer being treated. The antigen-loaded dendritic cells are then injected back into the patient, usually through subcutaneous or intradermal routes.
- Mechanism of Action of Dendritic Cell Vaccination
Once inside the body, the engineered dendritic cells migrate to the lymph nodes, where they present the tumor antigens to T cells. As a result this interaction stimulates the T cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells expressing these antigens. The result is a targeted immune response aimed directly at the tumor, sparing normal cells and minimizing side effects compared to conventional therapies like chemotherapy and radiation.
- Clinical Applications and Efficacy
Dendritic cell-based immunotherapy has shown promise in treating various cancers, including melanoma, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, breast cancer, and glioblastoma. Clinical trials have demonstrated that patients receiving dendritic cell immunotherapy can experience prolonged survival and improved quality of life.
- Challenges and Future Directions
Therefore, combining dendritic cell immunotherapy with other treatments, such as checkpoint inhibitors or conventional therapies, is being explored to enhance efficacy. Advances in genetic engineering and bioinformatics may also enable the development of more potent and precisely targeted dendritic cell vaccination.
What are the side effects of the dendritic cell vaccine?
Dendritic cell (DC) vaccination is an emerging immunotherapy for cancer used primarily to treat cancer by stimulating the immune system to recognize and destroy tumor cells. While generally well-tolerated, it can have some side effects, though these are typically mild compared to traditional cancer treatments like chemotherapy or radiation.Common side effects include:
- Injection site reactions: Redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site is common.
- Flu-like symptoms Fatigue, fever, chills, and muscle aches may occur as the immune system is activated.
- Fatigue: Some patients experience general tiredness, which can last for a few days after treatment.
Less common or more severe side effects:
- Autoimmune reactions: Since Dendritic Cell Vaccination for cancer boost immune activity, there’s a potential risk of triggering autoimmune responses, where the immune system attacks healthy tissues.
Overall, dendritic cell vaccines for cancer is considered safe, with most side effects being mild and temporary. Ongoing research aims to optimize its effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects. Close monitoring during treatment with the immunotherapy for cancer helps manage these risks effectively.
Game-Changing Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer Unleashed
Experts from the clinic collaborated with several European Universities and the biotech industry to develop unique and patented anti-cancer vaccines to treat cancer. It’s derived from a patient’s immune cells that can be easily obtained from peripheral blood. These cells are cultured in vitro to obtain dendritic cells.
Furthermore, dendritic cells are professional cells of the immune system capable of inducing strong anti-cancer responses. On some occasions, it is also beneficial to obtain freshly removed tumor tissue from patients undergoing elective surgery. However in case, the autologous tumor tissue is not available, allogeneic tumor cell lines characterized for the presence of universal tumor-associated antigens can be provided instead as a source of tumor antigen.
In general, there are no serious side effects associated with the vaccine. Your quality of life may improve dramatically. Therefore, this type of vaccine can be also produced and administered in earlier stages of cancer to enhance immune system activation in a fight with tumor cells without significant side effects. Read more about dendritic cell vaccines for cancer on Wikipedia.
Effective Dendritic Cell Therapy – Immunotherapy for Cancer
However, today we know that the immune system of patients with a low tumor mass is often still much more efficient than that of patients with high tumor load. Just like in chemotherapy and radiation, the faster dendritic cell vaccines for cancer begins, the more successful it is. However, to see if you are a candidate for dendritic cell vaccines for cancer in Germany and forward your medical reports to us.
Medical conditions that can be treated by dendritic cell vaccination:
- Dendritic cell therapy for Breast cancer
- Cervix and Uterus carcinoma
- Lung cancer and carcinoma
- Carcinoma at stomach
- Large intestine carcinoma (colorectal)
- Dendritic cell therapy for Pancreatic cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Stomach cancer
Indications that can be treated by dendritic cells – Immunotherapy for cancer:
- Glioblastoma
- Prostate Cancer
- Sarcoma of soft tissue
- Sarcomas of bone
- Ewing sarcoma
- Colon Cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Liver cancer
- Bladder carcinoma
What is the success rate of the dendritic cell vaccine?
The success rate of dendritic cell vaccines for cancer can vary significantly depending on the specific type of cancer being treated, the stage of the cancer. Furthermore, the individual patient’s response to the treatment. Dendritic cell vaccines for cancer in Germany are a form of immunotherapy for cancer designed to enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells.
The success of dendritic cell vaccinination can be influenced by several factors, including:
– The cancer type (e.g., glioblastoma, prostate cancer, melanoma, bladder cancer, lung cancer or breast cancer)
– The patient’s overall health and immune system status
– The method of vaccine preparation and administration
– The use of combination therapies (e.g., with checkpoint inhibitors)
It’s important to note that clinical trials are still assessing the long-term effectiveness and potential improvements in dendritic cell-based therapies.
Clinical Trials – Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer
Trial watch: Dendritic cell (DC)-based immunotherapy for cancer
Dendritic cells and immunity against cancer
A Dendritic Cell Vaccination Was Safe and Immune Responses in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Final results of brain cancer glioblastoma clinical trial
Antitumour dendritic cell vaccination in a priming and boosting approach
Dendritic cell vaccines in breast cancer: Immune modulation and immunotherapy
New hopes for the breast cancer treatment: perspectives on the oncolytic virus therapy
Dendritic cells and immunity against cancer
Research on dendritic cell therapy for AML (acute myeloid leukemia) has shown promising results
Vaccine-based immunotherapy for pancreatic and colon cancers
Advances in Vaccine-Based Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer
Harnessing dendritic cells for pancreatic cancer immunotherapy: a novel promising approach
Conclusion
Our program for dendritic cell vaccines in Germany we provide differs depending on the patient’s situation and history. As a result, most immunotherapy experts recommend a mix of treatments. This could be a combination of immune system strengthening therapy and dendritic cells dcs.A single dendritic cell (DC) therapy session may not be sufficient because the immune system needs repeated stimulation to mount and maintain a robust, long-lasting anti-cancer response. Just as with traditional vaccines, multiple treatments (sometimes called “boosters”) are often needed to build and strengthen immunological memory against cancer cells.
Why multiple Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer in are beneficial?.
The following factors illustrate why more than one dendritic cell therapy session may be necessary:
- Strengthening the immune response: A single dose may only prompt a limited or short-term immune reaction. Multiple dendritic cell vaccines for cancer doses, given over a period of weeks or months, can amplify this response, leading to more T-cells trained to recognize and attack the cancer. This process helps overcome the cancer’s natural ability to suppress immune attacks.
- Generating immunological memory: The goal of vaccination is to establish long-term memory cells. These cells allow the immune system to recognize and attack the cancer if it returns. Repeat vaccinations help create and reinforce this immunological memory, increasing the chance of a durable response and preventing relapse.
- Overcoming tumor evasion strategies: Cancer cells can be highly effective at evading immune detection. Hence, the anti-tumor immune response generated by dendritic cell vaccines for cancer can be thwarted by the “immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment”. Therefore, multiple treatment cycles can help counter these evasive tactics by providing a repeated surge of immune cells.
- Addressing tumor heterogeneity: Tumors can contain a mix of different cancer cells (known as tumor heterogeneity). A dendritic cell vaccines for cancer may target some cells effectively, but others may escape. However, using multiple DC vaccines loaded with a variety of antigens can create a broader immune attack, reducing the chances of cancer cells escaping.
- Enhancing combination therapy: In many cases, dendritic cell therapy is combined with other treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, or Immungentic Cell Death (ICD) giro-therapy. Timing the treatments correctly is crucial for boosting efficacy. Hence, multiple dendritic cell vaccines for cancer can be strategically scheduled alongside other treatments to enhance the overall anti-cancer effect.
Watch out! When Dendritic Cell Vaccines is offered in Mexico!
Dendritic cell cancer vaccine market is a huge problem! For example, the clinics in Mexico having NO LICENSE for producing dendritic cells. Although there is no official governmental office which is controlling those clinics.
In Germany every clinic has an annually audit by the German government to make sure they follow the legal standards. Though in Germany dendritic cell vaccines for cancer is safe and you get high quality!
How to book dendritic cell vaccines for cancer in Germany
With our specialized patient service, you find the best Clinic for dendritic cell vaccines for cancer in Germany. We set up your cost estimate and phone call with the doctor who is attending to you. After all, there shouldn’t be any unanswered questions about dendritic cell based vaccines in Germany.

We provide our personal assistance service to clients who are less experienced travelers abroad. This covers full service within the organization, clinic admission, airport transportation, and if required, a translation service. As a result, we also assist you with hotel reservations and visa applications.
Thanks to GermanyHealth, you can relax and prepare for your travel.Get all by one hand organized through our patient services. Our offer includes all from A to Z including transportation if you need it.
1. Personalized Patient Assistance: One of their standout features is their concierge services, offering personalized support throughout the treatment process. This includes:
– Help with travel arrangements (flights, transportation)
– Organizing accommodation close to medical facilities
– Guidance and assistance with language barriers during medical consultations
2. Access to Renowned Medical Institutions: Through their network, GermanyHealth helps patients access leading medical institutions known for cutting-edge technology and skilled professionals, often offering treatments not readily available in other countries.
Overall, GermanyHealth is best known for streamlining the healthcare process for international patients providing a seamless experience from travel logistics to treatment and recovery.

Request now and Book later!
Find the best Clinic for Immunotherapy for Cancer in Germany.
